Allow Apps From Unknown Sources Mac Terminal
- Mac Allow Apps From Anywhere
- Allow Installation Of Apps From Unknown Sources Mac Terminal
- Allow Apps From Unknown Sources Mac Terminal 2
- Allow Apps From Unknown Sources Mac Terminal Linux
Using the Terminal is the best way to allow installation of applications on your Mac without the tedious process involved in making exceptions for each one of them. Using this method, you can install and use applications as you wish regardless of their source. Opening apps from unidentified developers are not for everyone. MacOS Sierra changed the way your Mac handles applications from unidentified developers. It's now stricter with installing such apps than previous versions of OS X, but there are ways to get. App download preferences. At the bottom of the General screen are two options relating to which apps can run on your Mac. The safest, but most limiting option, is to only allow apps from the App.
If you’ve ever tried to open an app from an unidentified developer on your Mac, you know that it can be a tricky task. macOS has security measures in place that block this action in the hopes of protecting you from malware. That being said, it’s not impossible.
Here, we’ll talk about apps from unidentified developers and show you how to allow them on your Mac. We’ll also go over some tips for staying safe when downloading new software.
What is an unidentified developer?
An unidentified developer is an app developer that isn’t registered with Apple. Generally, apps from unidentified developers haven’t been reviewed by Apple for safety and security.
Apple believes that one of the easiest ways to distribute malware is to insert its code into an app. That’s why they check apps thoroughly before allowing them to release to the Mac App Store. Apps from unidentified developers aren’t on the App Store.
This doesn’t mean that apps from unidentified developers are malicious (although they can be). They can either not comply with Apple guidelines, or be created before the ID registration started.
Why your Mac shows a warning?
In order to protect your device from dangerous apps, Apple includes security measures in their devices. One example of this is Gatekeeper. Gatekeeper is Apple’s program that recognizes whether an app has been downloaded from the App Store. This program warns you when you’ve downloaded and attempted to run software from another location for the first time.
When you receive a warning about an app, it’s because Gatekeeper flagged it as a potentially dangerous app. This doesn’t necessarily mean that the app has malware—it simply means that macOS doesn’t recognize the app (or the developer). Because of this, you won’t be able to open the app as easily as you would an app that’s been vetted and listed on the App Store.
Luckily, it’s a bit easier to download apps from unidentified developers onto your Mac than onto other Apple devices.
How to set your Mac to allow apps from unidentified developers
By default, your Mac is set to block you from opening apps that haven’t been verified by Gatekeeper. This includes both apps that aren’t from the Apple App Store and those that come from unidentified developers.
It’s a good idea to start by first setting your Mac to allow you to open apps that aren’t from the App Store.
Setting your Mac to open apps not from App Store
By setting your Mac to open apps that aren’t from the App Store, you reduce the number of warnings you’ll get when opening third-party applications. This makes it much easier to open these kinds of apps.
Here’s how to change your Mac settings to allow apps from third-party locations:
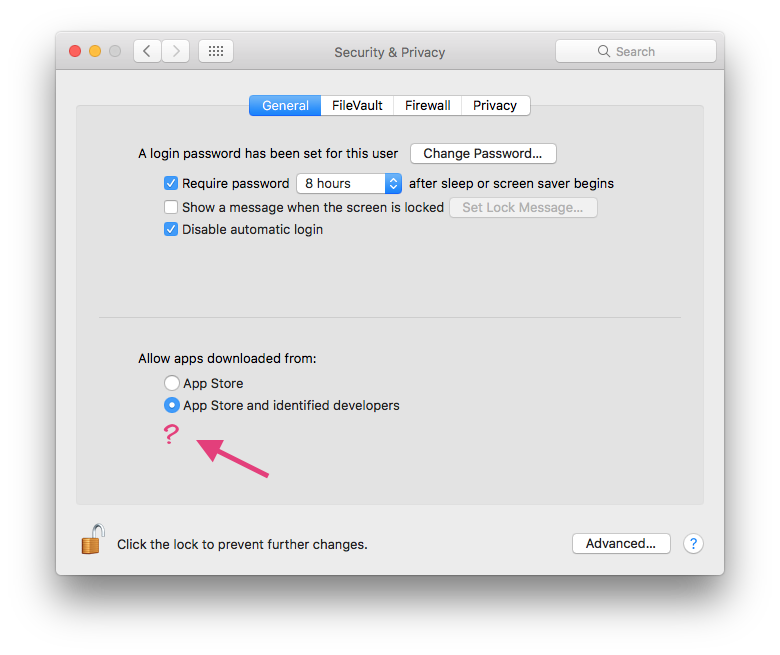
- Open your Mac’s System Preferences.
- Click on Security & Privacy, then go to the General tab.
- On the bottom left, you’ll see a padlock icon. Click on it and enter your admin password.
- Under “Allow apps to be downloaded from”, select App Store and identified developers.
Once this is done, you’ll be able to open most of the apps that aren’t on the App Store. However, you still won’t be able to open apps that aren’t recognized by macOS.
Setting your Mac to open apps from unidentified developers
If you want your Mac to allow apps from unidentified developers, you’ll have to follow a few additional steps. Firstly, try to open the unrecognized application. You’ll see a notification that it can’t be opened. Then, follow the instructions:
- Open System Preferences.
- Click on Security & Privacy, then go to the General tab.
- You’ll see the message “[App] was blocked from opening because it is not from an identified developer.” Clicking the button next to it marked “Open Anyway.”
- You’ll be asked again if you’re sure you’d like to run the app. Click the Open button to run it.
These steps allow you to open this app whenever you’d like. You should remember, though, that Gatekeeper won’t allow you to open apps that contain malware, even after following these steps.
Apple’s recommended way to open apps from an unidentified developer
Apple knows that Mac users still want to open apps from unidentified developers. Luckily, they’ve provided a method for doing so.
Here’s how:
- Go to your Mac’s Finder.
- Find the app you tried to open. If you’re having a hard time finding it, you can search for it in Finder or using Spotlight search (Command-Space).
- Right-click on the app.
- On the menu that pops up, click Open, and the app will open like any other.
Following these steps will make this app an exception, allowing you to open it again.
Opening apps from anywhere
Earlier versions of macOS used to provide the option to “allow apps from anywhere.” This would allow you to open any app without having to go through the above steps for each one you’d like to open.
While convenient, this can be dangerous, as it can leave your Mac open to malware. This is likely why it’s been hidden as a readily available option.
Are apps from unidentified developers safe?
Because they require circumventing Apple’s default security vetting process, it’s harder to determine whether apps from unidentified developers are safe. You’ll need to be sure yourself that a particular app can be trusted.
The best you can do to ensure that an app is safe to open is to do your research on it. Read through some reviews and look into the experiences other users have had with the app, as these sources are the most likely to give you truthful and relevant information. Dig as deeply as you can to help avoid downloading any dodgy apps.
You should also ensure that you have antivirus software (and that it’s up to date). This adds an extra layer of protection to your Mac. If you find that an app isn’t trustworthy, opt for an alternative app in the App Store or one from an unidentified developer that you can trust.
Keep your Mac malware-free
Downloaded a suspicious app? CleanMyMac X allows you to check your Mac for potentially unwanted apps (PUA) and malware with its Malware Removal Module. This feature scans your Mac for malicious apps and allows you to delete them one-by-one or in bulk. CleanMyMac X also features a real-time malware monitor to help you keep track of whether you’re not downloading anything malicious.
Here’s how to use it:
- Get the app on your Mac.
- Launch CleanMyMac X and go to Malware Removal.
- Press Scan.
If CleanMyMac X has found any threats, press Remove to delete them. Additionally, you can free lots of space on your Mac by deleting outdated cache files, system log files, and other unused junk with the System Junk feature.
Now, you know how to install any app on your Mac and circumvent the restrictions. But, if you aren’t vigilant enough, you may need to deal with the consequences of malicious software. It’s a good idea to always question the apps you want to install and look for additional reviews and testimonials.
The Terminal app allows you to control your Mac using a command prompt. Why would you want to do that? Well, perhaps because you’re used to working on a command line in a Unix-based system and prefer to work that way. Terminal is a Mac command line interface. There are several advantages to using Terminal to accomplish some tasks — it’s usually quicker, for example. In order to use it, however, you’ll need to get to grips with its basic commands and functions. Once you’ve done that, you can dig deeper and learn more commands and use your Mac’s command prompt for more complex, as well as some fun, tasks.
Curated Mac apps that keep your Mac’s performance under control. Avoid Terminal commands, avoid trouble.
Download FreeHow to open Terminal on Mac
The Terminal app is in the Utilities folder in Applications. To open it, either open your Applications folder, then open Utilities and double-click on Terminal, or press Command - spacebar to launch Spotlight and type 'Terminal,' then double-click the search result.
You’ll see a small window with a white background open on your desktop. In the title bar are your username, the word 'bash' and the dimensions of the window in pixels. Bash stands for 'Bourne again shell'. There are a number of different shells that can run Unix commands, and on the Mac Bash is the one used by Terminal.
If you want to make the window bigger, click on the bottom right corner and drag it outwards. If you don’t like the black text on a white background, go to the Shell menu, choose New Window and select from the options in the list.
If Terminal feels complicated or you have issues with the set-up, let us tell you right away that there are alternatives. MacPilot allows to get access to over 1,200 macOS features without memorizing any commands. Basically, a third-party Terminal for Mac that acts like Finder.
For Mac monitoring features, try iStat Menus. The app collects data like CPU load, disk activity, network usage, and more — all of which accessible from your menu bar.
Basic Mac commands in Terminal
The quickest way to get to know Terminal and understand how it works is to start using it. But before we do that, it’s worth spending a little time getting to know how commands work. To run a command, you just type it at the cursor and hit Return to execute.
Every command is made up of three elements: the command itself, an argument which tells the command what resource it should operate on, and an option that modifies the output. So, for example, to move a file from one folder to another on your Mac, you’d use the move command 'mv' and then type the location of the file you want to move, including the file name and the location where you want to move it to.
Let’s try it.
Type cd ~/Documentsthen and press Return to navigate to your Home folder.
Type lsthen Return (you type Return after every command).
You should now see a list of all the files in your Documents folder — ls is the command for listing files.
To see a list of all the commands available in Terminal, hold down the Escape key and then press y when you see a question asking if you want to see all the possibilities. To see more commands, press Return.
Unix has its own built-in manual. So, to learn more about a command type man [name of command], where 'command' is the name of the command you want find out more about. /force-quit-app-mac.html.
Terminal rules
There are a few things you need to bear in mind when you’re typing commands in Terminal, or any other command-line tool. Firstly, every character matters, including spaces. So when you’re copying a command you see here, make sure you include the spaces and that characters are in the correct case.
You can’t use a mouse or trackpad in Terminal, but you can navigate using the arrow keys. If you want to re-run a command, tap the up arrow key until you reach it, then press Return. To interrupt a command that’s already running, type Control-C.
Commands are always executed in the current location. So, if you don’t specify a location in the command, it will run wherever you last moved to or where the last command was run. Use the cdcommand, followed by a directory path, like in Step 1 above, to specify the folder where you want a command to run.
There is another way to specify a location: go to the Finder, navigate to the file or folder you want and drag it onto the Terminal window, with the cursor at the point where you would have typed the path.
Here’s another example. This time, we’ll create a new folder inside your Documents directory and call it 'TerminalTest.'
Open a Finder window and navigate to your Documents folder.
Type cd and drag the Documents folder onto the Terminal window.
Now, type mkdir 'TerminalTest'
Go back to the Finder, open Text Edit and create a new file called 'TerminalTestFile.rtf'. Now save it to the TerminalTest folder in your Documents folder.
In the Terminal window, type cd ~/Documents/TerminalTest then Return. Now type lsand you should see 'TerminalTestFile' listed.
To change the name of the file, type this, pressing Return after every step:
cd~/Documents/Terminal Test
mv TerminalTestFile TerminalTestFile2.rtf
That will change the name of the file to 'TerminalTestFile2'. You can, of course, use any name you like. The mv command means 'move' and you can also use it to move files from one directory to another. In that case, you’d keep the file names the same, but specify another directory before typing the the second instance of the name, like this:
Mac Allow Apps From Anywhere
mv ~/Documents/TerminalTest TerminalTestFile.rtf ~/Documents/TerminalTest2 TerminalTestFile.rtf
More advanced Terminal commands
Terminal can be used for all sorts of different tasks. Some of them can be performed in the Finder, but are quicker in Terminal. Others access deep-rooted parts of macOS that aren’t accessible from the Finder without specialist applications. Here are a few examples.
Copy files from one folder to another
In a Terminal window, type ditto [folder 1] [folder 1] where 'folder 1' is the folder that hosts the files and 'folder 2' is the folder you want to move them to.
To see the files being copied in the Terminal window, type -v after the command.
Download files from the internet
You’ll need the URL of the file you want to download in order to use Terminal for this.
cd ~/Downloads/
curl -O [URL of file you want to download]
If you want to download the file to a directory other than your Downloads folder, replace ~/Downloads/ with the path to that folder, or drag it onto the Terminal window after you type the cd command.
Change the default location for screenshots
If you don’t want macOS to save screenshots to your Desktop when you press Command-Shift-3, you can change the default location in Terminal
defaults write com.apple.screencapture location [path to folder where you want screenshots to be saved]
Hit Return
killall SystemUIServer
Hit Return
Change the default file type for screenshots
Allow Installation Of Apps From Unknown Sources Mac Terminal
By default, macOS saves screenshots as .png files. To change that to .jpg, do this:
defaults write com.apple.screencapture type JPG
Press Return
killall SystemUIServer
Press Return
Delete all files in a folder
The command used to delete, or remove, files in Terminal is rm. So, for example, if you wanted to remove a file in your Documents folder named 'oldfile.rtf' you’d use cd ~/Documents to go to your Documents folder then to delete the file. As it stands, that will delete the file without further intervention from you. If you want to confirm the file to be deleted, use -i as in rm -i oldfile.rtf
To delete all the files and sub-folders in a directory named 'oldfolder', the command is rm -R oldfolder and to confirm each file should be deleted, rm -iR oldfolder
Just because you can use Terminal to delete files on your Mac, doesn’t mean you should. It’s a relatively blunt instrument, deleting only those files and folders you specify.
Allow Apps From Unknown Sources Mac Terminal 2
Another way to free up space
If your goal in removing files or folders is to free up space on your Mac, or to remove junk files that are causing your Mac to run slowly, it’s far better to use an app designed for the purpose. CleanMyMac X is one such app.
It will scan your Mac for files and recommend which ones you can delete safely, as well as telling you how much space you’ll save. And once you’ve decided which files to delete, you can get rid of them in a click. You can download CleanMyMac here.
As you can see, while Terminal may look scary and seem like it’s difficult to use, it really isn’t. The key is learning a few commands, such as those we’ve outlined above, and getting to know the syntax for those commands.
However, you should be careful when using Terminal, it’s a powerful tool that has deep access to your Mac’s system files. Check commands by googling them if you’re not sure what they do. And if you need to delete files to save space, use an app like CleanMyMac X to do it. It’s much safer!